“Evaluation and analysis of mechanical industry: creative and innovative development of enterprises in the context of investment resources deficiency”
Murinovich Dariana
MBA
Head of GR unit
JSC «Integrated Thermal Power Company»
DBA program student
the Russia Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration
Russia, Moscow
e-mail: darianamurinovich@gmail.com.
Prazdnov Gennady
doctor of economics
professor of the department of inter branch enterprises
Institute of Industrial Management
the Russia Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration
Russia, Moscow
e-mail: prazdnov@ranepa.ru.
Abstract:
Mechanical industry is the industry providing innovative development of enterprises in all sectors of the national economy. For that reason, mechanical engineering needs accelerated flow of investment aimed to introduce creative innovations intended for large-scale technical re-equipment and modernization of existing industries.
Outdated main production assets (MPA), insufficient financing, high competition in both – domestic and foreign markets, as well as lack of qualified personnel, reduce the possibilities for accelerated development of machine-building enterprises.
Insufficiency of existing methodology for assessing and analyzing susceptibility to innovations; lack of flexibility and adaptability to innovations and market needs, and of systematic management of the MPA update process, as well as implementation of scientific achievements and the intellectual potential of workers – all these restrain innovative development of mechanical industry.
Improved methodology for both – objective and comprehensive assessment of the state and dynamics of innovative development, based on materials of machine-building enterprises in Ural Federal District, is proposed in the article.
Key words:
Mechanical engineering, machine-building, mechanical engineering, investment, innovation, development, evaluation system, flexibility, adaptability, creativity, importance of science, intellectual level, efficiency.
Introduction.
Russia needs qualitative transformation of productive potential from the resource type to creative and innovative type of economic development.
The new model of economic development considers a shift of focus to the development of innovation and intellectual property market. It is not only about using, but first of all about the development of innovations within the country to meet the needs of the domestic economy development.
The importance of developing an innovative economy for our country is explained by the increasing competition with industrialized and developing countries which have lower prices and higher quality characteristics of their products.
With a high demand for innovations in all sectors of Russia’s economy and budget possibilities, the implementation of innovation-based fundamental renewal of the country’s productive potential does not meet the needs of the domestic market.
The purpose of the article is to consider the specifics of machine-building enterprises innovative development in the context of limited funding, instability in demand and prices, as well as increasing competition. Criteria, algorithm, and system of indicators for assessing the susceptibility of economic entities to modern innovations are substantiated in the article; and dependence of creative, flexible and adaptive machine-building enterprises development on innovative development is also revealed.
Main objectives: analysis of the state and dynamics in terms of innovations necessity, identification of the need and possibilities for increasing the level of susceptibility to innovations, making recommendations on improving financing, stimulation and learning management system for increasing the susceptibility of enterprises to innovations.
The object of the research: industry oriented economic units of Ural Federal District.
Main part.
Mechanical engineering is the core of industry, designed to provide machinery and equipment for all sectors of economics, thereby determining the production potential of the national economy. A significant number of workers is concentrated in mechanical engineering (40% of all employed in industry). The share of the industry (about 25%) in gross domestic product output is large. [1].
Material consumption, energy intensity of products, labor productivity, production efficiency, safety and state defense capacity depend on the development of mechanical engineering. Technological change in the sectors of the country’s economy is materializing through mechanical engineering products, especially machine tools, electrical and instrument engineering.
All over the world, innovation acts as the material basis for improving production efficiency, quality and competitiveness of products. The growth of high-tech industries, increasing the role of intellectual capital, strengthening the role of human dimension are the signs of this process. At the same time, the most important resource of any state is science, which determines the essence of economic policy, the tasks and methods of its implementation. It is not by chance that such prominent economists as M. Friedman, D. Galbraith, A. Laffer, P. Samuelson and others acted as economic advisers to the Presidents of the United States.
The integral indicator of the enterprise’s innovative development is the volume of exports of high-tech and science-intensive production. The annual turnover on the world market for such products is several times higher than the turnover of the market for raw materials, including oil, oil products, gas and wood. It’s about trillions of dollars. Unfortunately, Russia’s share in this market is very poor — 0.25–0.3% (30th place, 6.6 billion dollars). [2]. To compare, China’s share is 16.3%, the USA share is 13.5%. [3].
Russia’s goal in the near future is to turn into advanced industrialized economic nation, therefore there is no alternative to strategic direction of the mechanical engineering development. For the successful solution of this kind of global challenge it is necessary to consolidate the scientific and production potential. An innovative strategy links together the processes of staff capacity and resource potential development of the enterprise and specific innovative projects. Innovative development of production should be based on updating the knowledge of workers, which would be adequate to innovations.
At present, mechanical engineering in Russia is clearly not playing the role of the national economy productive forces innovative development moderator. The presence of a large amount of physically obsolete and morally obsolete production facilities, very low level of technological equipment at workplaces, an insufficient degree of flexibility and adaptability of enterprises to innovations and market needs, and, as a result, unsatisfactory production efficiency indicators require a fundamental change in the investment policy of both, public and private entities.
Russian machine-building industry production provides the needs of the national economy only by 60%, and by 15% for selected high-quality machines and technical systems. Some types of equipment such as computers and video equipment are not produced at all. Products with microprocessor technology give only 6.7% of the total number. And only 12% of products meet the external market requirements. Talking about physical structure, the share of progressive materials does not exceed 4%, in comparison to 18-20% in the USA. [4]. This is happening due to the lack of active development and introduction of innovative breakthrough technologies. In this regard, the major trust of mechanical engineering development strategy is accelerated innovation-driven development. The share of innovatively active enterprises in Russia is still less than 9% against 30–50% in advanced industrial countries. At the same time, almost 24% of Russian companies receive federal funding for technological innovations. In foreign countries, the ratio isopposite: the share of innovatively active companies exceeds the share of companies receiving federal funding. [5].
The methods used in Russia for assessing the innovative development of machine-building enterprises consider a number of private and integral indicators which do not fully characterize the state and dynamics in enterprise’s technical and intellectual capacity.
The relevance and importance of developing a universal methodology for assessing and analyzing the innovative development of machine-building enterprises predetermines the need to improve the existing methodology.
A critical link for innovation development is technical re-equipment, which, in our opinion, should be divided into two types. The first one is the replacement of obsolete equipment by new equipment of similar kind. In many cases, this is sufficient for the purpose of modernization.
Second type technical re-equipment involves the replacement of obsolete technology with a fundamentally new one, more productive and efficient. This is what is meant by the process of creative innovation development.
From the investment point of view, the innovation boundaries should be determined by the value zone, which lies between 2 and 10% of the replacement (market) cost of the enterprise implementing any kind MPA. The introduction of innovations less than 2% should be attributed to the improvement, and above 10% — to the creative innovation development.
This article proposes the use of indicators that complement and expand the boundaries of the innovat existing ion development assessment, contributing to the identification and full use of innovation capacity reserves.
Below are formula examples for the calculation of several proposed indicators.
Ratio of turnover (R) of capital-labor ratio at subsidiary (S) and main (M) productions.
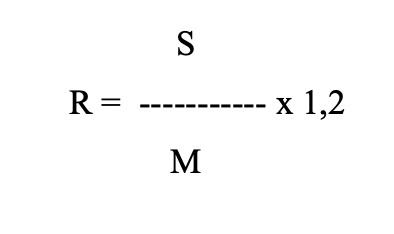
S and M – capital-labor ratio, respectively, in subsidiary and main divisions of the enterprise, rubles/person;
1,2 — acceptable level gap coefficient between S and M.
Enterprise flexibility coefficient (EFC) to the needs of the market:
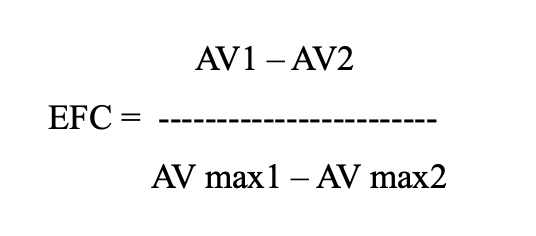
Here: AV1 and AV2 — added value of the reporting enterprise for the revised period and in the past, rubles.
AV max1 and AV max2 — added value of the best out of all revised enterprises for the revised period and in the past, rubles.
Any enterprise has flexibility to the market needs if, first of all, it did not show any reduce of produced added value in the revised period, compared to the baseline, and, secondly, this value is comparable to the reference value achieved at the best by this indicator enterprise.
Enterprise adaptability coefficient (EAC) to the market needs:
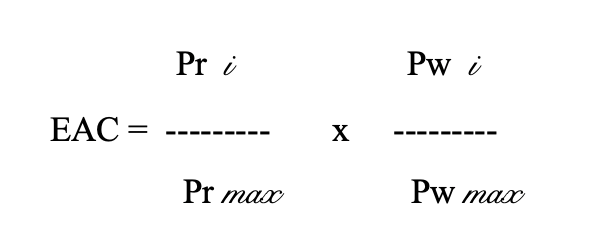
Here: Pr i, Pw i, Pr max, Pw max — profit earned per worker and one ruble value of MPA at the revised enterprise and at the best out all revised enterprises, rubles/person for both. Enterprise which is considered to be adaptive to the needs of the market is the one, where the profit per worker and per MPA unit cost is constantly increasing.
By integrating the proposed indicators, the levels of innovation development (LID) were calculated for a group of revised machine-building enterprises in Sverdlovsk region.
| Coefficient | Level of coefficients, % | Change of coefficients | |
| 2012 | 2017 | ||
| PC utilization C | 100 | 1,108 | 1,108 |
| R | 100 | 1,101 | 1,101 |
| EFC | 100 | 101,0 | 101,0 |
| EAC | 100 | 0,996 | 102,2 |
| LID | 100 | 105,0 | 107,0 |
Table 1. The levels and changes in the coefficients of innovation development calculated for a group of enterprises in Sverdlovsk region.
The authors’ calculations indicated the following: by increasing the level of production capacity (PC) use, improving the age characteristics of the active part of production assets, increasing the degree of flexibility and adaptability to market demands, it is possible to slightly increase the level of innovation development (which is not completely “caught” under the previous evaluation system) . This will lead to the labor productivity improvement (5.8% increase), profitability (3.1% increase), reduction of production costs (1.9%).
The logical conclusion of the applied methodology for assessing the innovative development of enterprises is the examination of the increase in capital investment (C) on production efficiency effect. The task is set in the following way: to find out by what amount LID will increase, if 10, 20 … N million (billion) C rubles are spent.
According to our calculations, LID of one of the revised enterprises – “Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant — Uraltrak LLC” (CHTZ-URALTRAC) is 0.72 (with a limit value equal to one), and this allows to have a profitability of about 12% (data as of 2016). Increasing LID to 0.73 will increase profitability to 13.5%. You only need to calculate how much investment is required in order to achieve this particular result.
In our opinion, the problem of accelerating the development of mechanical engineering in Russian Federation can be explained by the lack of scientific and methodological substantiation of the applied strategies for innovation development. The availability of clear science-based conceptual approaches to the formation of industry-oriented economic entity at the modern and qualitatively new level, as well as building strategy for its renewal and development can greatly facilitate and significantly accelerate creative innovation development of the whole country.
Russia ranks tenth in the ranking of the leading countries in terms of domestic expenditures on research and development based on the purchasing power parity of national currencies. In 2016, it amounted to $ 39.9 billion. In terms of the share of expenditures on science in gross domestic product (1.1%), Russia lags significantly behind the leading countries, being in 34th place.
The development of science depends on financial investments. The more financial resources allocated by the state and business structures to science, the more effective the results of scientific achievements. In 2016 Russia’s expenditures on research and development institutes amounted to about 1 trillion rubles, which is significantly inferior in this indicator to the leading industrialized countries, such as the United States, China, Japan [6].
Unfortunately, as for now, the number of innovatively active enterprises in Russia is less than 9% against 30-40% in industrialized countries. At the same time, almost a quarter of domestic companies receive federal funding for technological innovations. In industrialized countries, the number of companies receiving government funding is much smaller.
Conclusions.
1. The need for innovative development of machine-building enterprises is determined by the growing needs in engineering products, the TFR deterioration, as well as the increased market competition.
2. Factors hindering the creative, innovative development of mechanical engineering in Russia are the following: insufficiently developed methodology for assessing and analyzing innovative development, the low level of enterprises’ susceptibility to innovations, insufficient financing of innovative processes, the low degree of flexibility and adaptability of most enterprises to innovations and market needs. The development and introduction of innovative breakthrough technologies, the lack of close ties and cooperation with scientific institutions, the lack of highly skilled professionals for creating innovative development programs and specialists who can implement existing programs are clearly insufficient. It is necessary to increase the level of state investment on research and development; ensure the protection of intellectual rights, and increase the level of remuneration for work of employees involved in research and development fields.
REFERENCES:
1. The number of operating enterprises, the average annual number of employees, GDP, MPA, profitability. Russia in numbers 2017.
2. Export and import of the Russian Federation. Russia in numbers 2017, pp. 473, 474, 484, 486.
3. Radzikhovsky L. Running from time. Russian newspaper. 04.09.2018
4. Ivanchenko A., Ushakov D. Complex of development tendencies of the global market for high-technology products. Young scientist. 2018 — №17 c. 171-173.
5. Innovatively active enterprises in Russia. Institute of Economic Policy.
E. Gaidar. Russian economy in 2016. (Issue 38). Gaidar Institute publishing house. M.: 2017.
6. Young scientist №47 (233) November 2018.